Architecture Overview
Understand how Pantheon Content Publisher works, the different parts it is made of, and how it can fit your organization.
Content Publisher is a SaaS solution that allows organizations to better manage their web publishing workflow from content creation to content delivery. Content Publisher is an API-first content integration service that connects and prepares content from various sources to be published on various web destinations. The service is built around a modern architecture, embracing composable architecture, leveraging the best of web APIs and GraphQL query language, and utilizing LLMs for content discovery and enrichment, design, and code delivery.
No matter the size or importance, all websites have a process of putting content on the site. This process often includes many activities such as writing meta information for SEO, optimizing media assets for fast delivery, linking content between each other, checking for usability and accessibility issues, and many more.
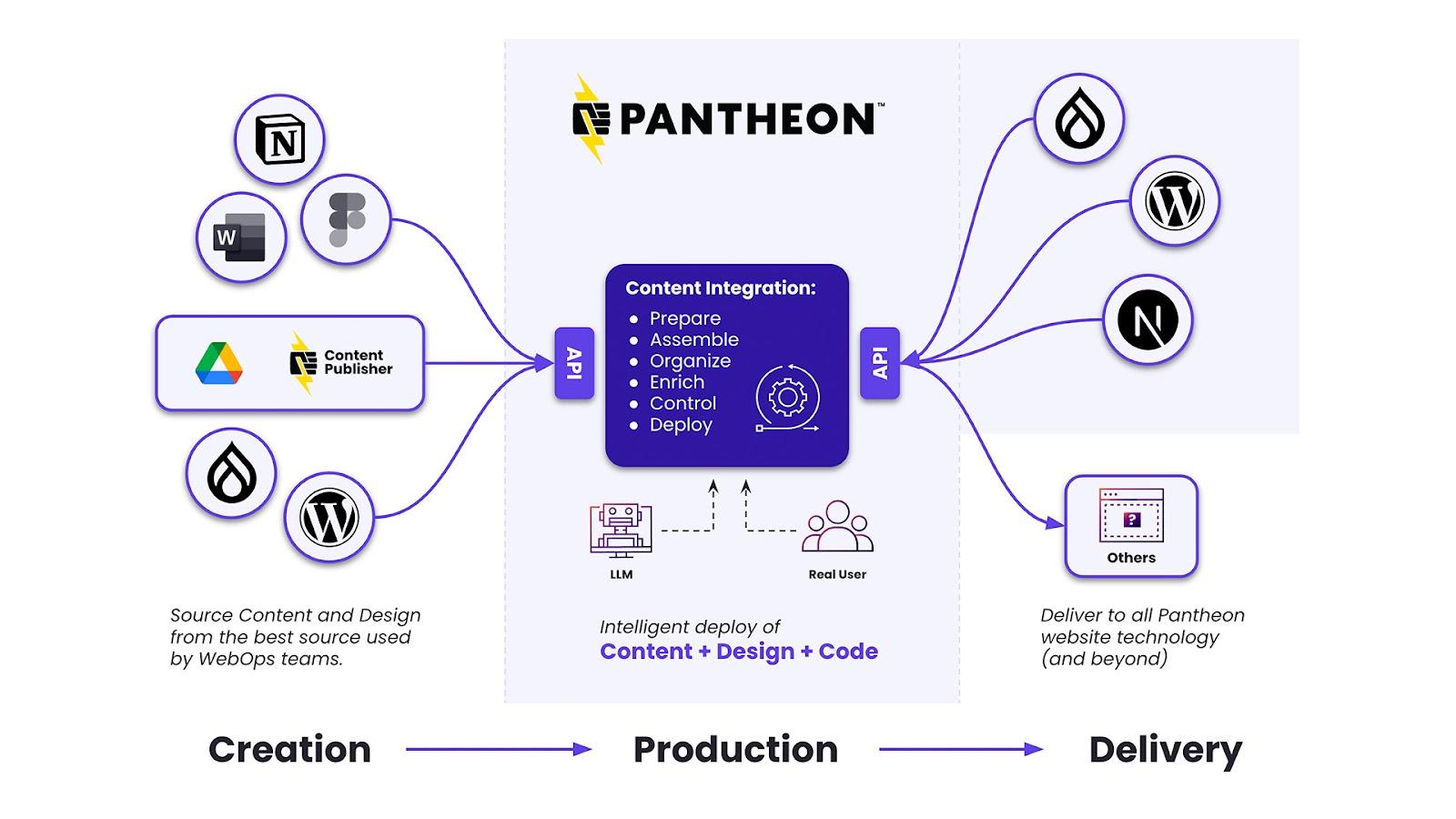
We see the publishing workflow as a three layers of functionalities:
Content Creation
This is the creative stage where content creators collaborate to shape content units, such as stories for news websites, documentation pages for product or service, personal blog posts, scientific papers or content marketing stories.
Content Production
Content Production refers to the discipline of preparing content for being published on the Web, and/or possibly on other digital channels. It is often managed by operators or content managers rather than the content creators themselves. It might include content enrichment, content optimization, content relation, fact checking, tone-of-voice checking, optimization of media (images, video and infographics) assets.
Content Delivery
Content delivery refers to the live website (or app) that is directly accessed by users. From a system and technology perspective, it is the part in charge of delivering the final web pages to the end-users. It is typically supporting the website architecture, design, performance and stability. It can involve numerous systems such as the web content management systems or framework (such as Drupal, WordPress or Next.js), the edge services such as CDNs, the personalization services and integration with other web services.
Content Publisher Workflow
At the content creation level, Content Publisher aims at “meeting users where they are”. Content Publisher is accessed by content creators directly in Google Docs, using the Pantheon Content Publisher add-on for Google Docs.
This add-on offers Google Docs users to access directly Content Publisher features such as previewing content, publishing content, managing its metadata, adding smart components inline in the document or more.
In the future, Content Publisher will support other content creation tools beyond Google Docs. We foresee that we will be able to support tools such as Google Sheet, Notion, Monday.com, Airtable or others. If interested in developing a solution for a tool you use or develop, please reach out.
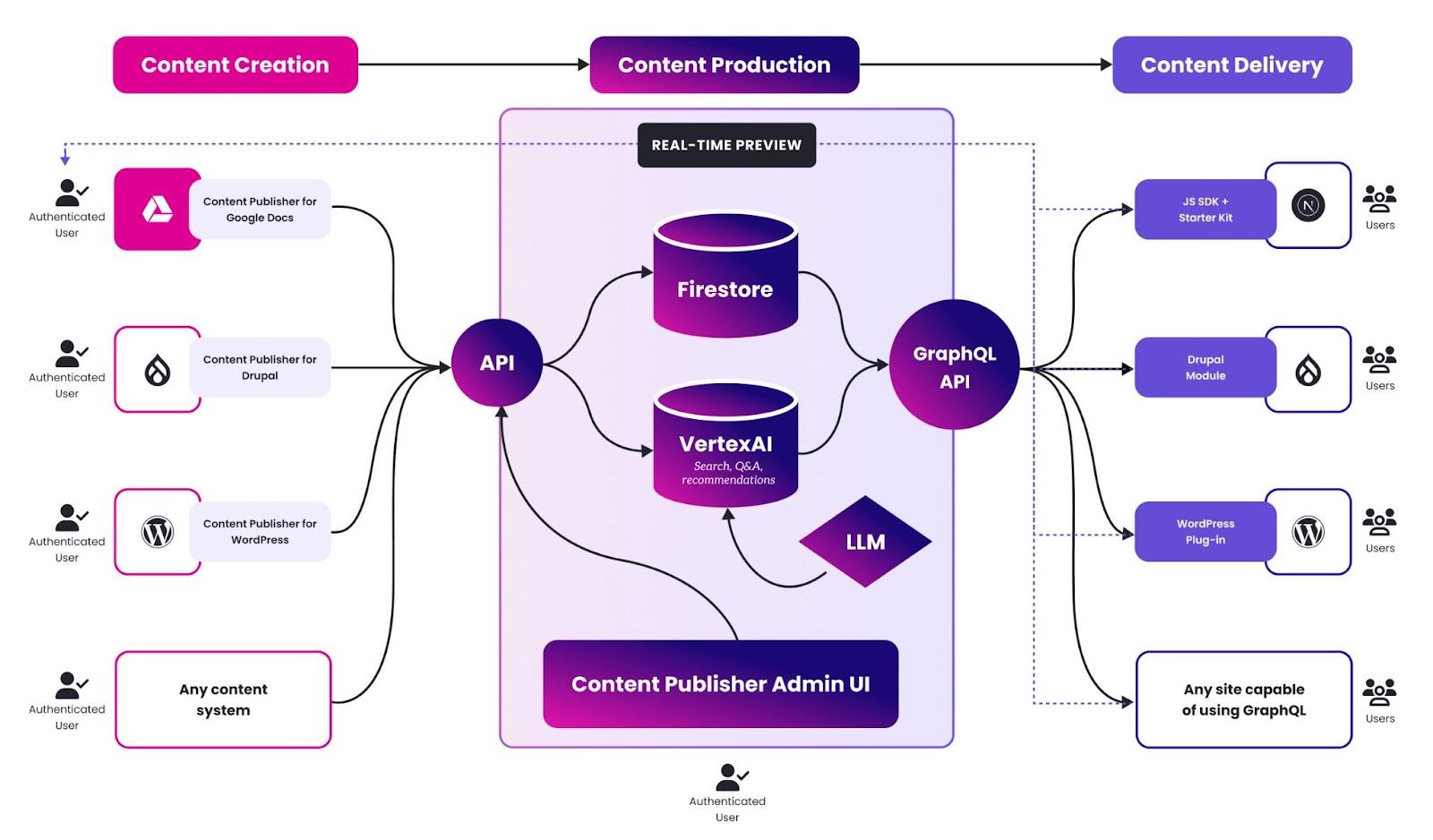
This is the core of Content Publisher. A service offering several interface:
- Ingest API:
This API allows the Google Docs add-on, and possibly any other content source to push content in Content Publisher for further publishing. The Ingest API is a modern public REST API and will be used by us and our partners and customers to build integration with content creation tools. - Delivery API:
This API exposes the content of a customer to its content delivery channels, including the ability to search for content. The delivery API is a GraphQL public API that can be used after authentication to pull and deliver content to end-users. The API allows users to pull content, content metadata and content structure as well as search for content including using Gen-AI augmented search. - Content Publisher Administration Interface:
The Administration interface is typically used by Content Managers and Content Administrators to perform many content management operations from creating content collections, managing permissions, metadata or organizing content collections. - Content Publisher CLI (command line interface):
The CLI is used by developers involved in projects to create and configure Content Publisher. Its capabilities overlap with the Administration Interface, exposing these capabilities to a technical persona.
From an architectural perspective, the solution is built based on cloud-native platform multi-tenant architecture. It currently fully leverages Google Cloud Platform although we remain open to deploying on other platforms if required.
Among others, content is ingested as Markdown documents which are stored in Firestore, search and gen-ai content discovery is leveraging Vertex AI which can be configured to run different LLM depending on the needs.
Content Publisher Architecture
Any digital experience platform with ability to connect and retrieve content from a GraphQL API could potentially be used to deliver content to users. For that, our Public GraphQL API is available and documented.
Nevertheless, we want to provide ease of use as well as ease of configuration. For that purpose, we support the main Website technology options on the market today, which are also available on Pantheon.io platform: Next.js, Drupal and WordPress.
- Next.js delivery
Use Content Publisher Next.js SDK or starter kit to deliver Content Publisher content in a Next.js website simply.
- WordPress delivery
Use Content Publisher WordPress plugin to simply configure your WordPress setup to publish content automatically from your Content Publisher collections as WordPress posts or pages. Installation is code-free and can be operational in a matter of minutes.
- Drupal delivery
Use Content Publisher Drupal modules to simply configure your Drupal (version 10+) to deliver content simply through the View system. Configuration does not require any development beside the possible templating you might want to implement for that purpose. Configuration requires understanding of the View system.